Medical male circumcision: Your questions answered
Medical male circumcision: Your questions answered
Is medical male circumcision safe?
In the hands of a well-trained, licensed medical professional, medical male circumcision is an extremely safe procedure. However, please remember that no surgery is without risks. The overall rate of procedural complications with medical male circumcision is low, reported to be less than one percent. Most of these complications are minor and can either be prevented by following instructions prior to the medical male circumcision or can be easily remedied by a healthcare provider if detected and treated early. For example, the most common complication is bleeding. To help prevent bleeding, please avoid aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for ten days before the medical male circumcision unless otherwise instructed by your physician. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications include common over-the-counter drugs such as ibuprofen, Advil, and Motrin. During the medical male circumcision, the healthcare provider can address bleeding by using pressure to the area, dissolvable stitches, or chemical agents that help seal blood vessels and promote clotting. By following post-procedure instructions, complications can be minimized. Patients may receive instructions regarding the use of antibiotic ointments to help promote healing and the performance of routine hygiene to keep the site clean and dry. It is very important not to go swimming or soak in a bath or hot tub until the doctor advises that it’s safe to do so, usually within five days. Even minor complications, if left untreated, can lead to the need for additional medical treatment. Examples of additional treatment could include antibiotics to address an infection or a second procedure to correct a problem. Now, it is important to keep the risks and complications in perspective. All surgeries have some degree of risk, but it is worth noting that medical male circumcision is one of the oldest and most studied surgical procedures in human history.
Is medical male circumcision painful?
It is possible that some boys and men experience pain or discomfort following the administration. The area will be sore, however, the pain can be effectively managed with over-the-counter pain relief prescriptions, for instance, paracetamol. It is basic to interfere with adequate fluid intake and to avoid alcohol for no under 24 hours after the operation. Men and boys who experience any kind of pain or distress that can’t be managed using over-the-counter remedies should contact their GP. This is an ensured, ordinary reaction to the minor surgery and it routinely settles after a few days. However, it is fundamental to watch out for searing or making pain, as this can indicate an inner burden and requires prompt medical attention. Pain or discomfort that flashes up seven days or longer after the operation can be a reaction of minor complications, for instance, a stitch getting caught in the skin. In case this happens, it is basic to seek advice from a GP or a sexual health specialist. This kind of inconvenience can be effectively managed and the sooner it is tended to, the better. These pieces of information and advice suggest that, similarly as with any surgery, there is some discomfort related to medical male circumcision. Nevertheless, there are different ways to manage and manage this, and most men and boys are back to their standard, everyday practices within a short space of time.
How is medical male circumcision different to other kinds of circumcision, like traditional or religious circumcision?
Medical male circumcision is different from other kinds of circumcision in that it is carried out for medical reasons, rather than as a traditional practice or for religious beliefs. Traditional or religious circumcision is usually carried out on newborn babies and is often performed by an experienced, trained older boy or adult, rather than a medical professional. In comparison, medical male circumcision is a surgical procedure carried out under anesthesia by a doctor, nurse, or clinical officer. This means it is a much safer procedure with a lower risk of complications. Because of this, medical male circumcision can be carried out on older boys or men, as well as newborn babies. The medical male circumcision procedure itself is also different from traditional or religious circumcision. When medical male circumcision is carried out, the foreskin is removed completely from the base of the penis. This is different from traditional circumcision, where the foreskin is sliced and peeled back but is not removed, and from religious circumcision, when only a small amount of the foreskin is removed.
Who does the procedure?
Circumcisions can be done by neonatal nurses, midwives, general practitioners, family physicians, pediatricians, obstetricians, and gynecologists at different points in their careers. Some circumcisions are also performed by anesthetists, which may be because a baby is being circumcised in a hospital, rather than in the community. In some traditions or religious ceremonies, circumcisions are performed by non-medically trained people. However, there is no evidence to support that this is a safe way for circumcisions to be carried out, and indeed such a procedure is likely to leave long-term pain and distress to the person being circumcised. Only qualified healthcare providers should perform circumcisions. This includes: medical doctors, nurse practitioners, obstetricians, family physicians, pediatricians, registered nurses, physician assistants or surgeons. It is important to check whether the person doing the procedure has had the appropriate training and experience in carrying out circumcisions. If the circumcision were being done in a hospital or private facility, both the person doing the procedure would have had their credentials checked and the facility would also have had to prove its competency and safety. This requirement reflects both the fact that circumcision is a significant operation and that mistakes can easily be made, especially when the people under the knife are too young to consent or understand what is being done to them.
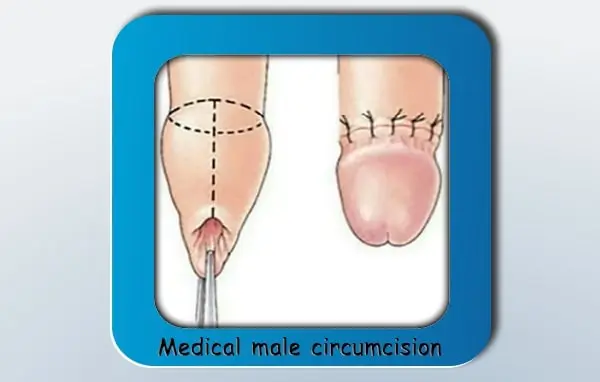
What are the benefits of medical male circumcision? Why should I have this done?
Having medical male circumcision can greatly reduce the chances of developing infections passed on during sexual intercourse. A circumcision can help reduce the risk of contracting HIV. Circumcised males are also less likely to suffer from urinary tract infections. Cultures that practice male circumcision have lower rates of cervical cancer in female partners. The risk of prostate cancer is also less in males who are circumcised. Foreskin-related conditions such as balanitis and phimosis will be prevented. Also, the physical problems associated with the foreskin can be avoided. These include a foreskin that is too tight, which causes painful erections and makes sexual intercourse uncomfortable. Persistent problems, including bleeding and infections caused by these conditions, can result in scarring of the genitals and the urinary opening becoming too narrow. In later life, this can cause problems passing urine. Being circumcised may make it easier to keep the end of the penis clean. However, it’s important to teach any child about the need for good hygiene, regardless of whether they are circumcised or not. Medical male circumcision usually requires only local anesthesia, and it’s a relatively simple procedure. The foreskin is removed quickly and the wound heals within a few weeks. However, full recovery will take up to four to six weeks. For the first couple of days after the operation, the penis will be sore and swollen. It is important to keep the area clean and to avoid any rigorous physical activities for up to six weeks. Sexual intercourse should also be avoided. It is up to you to decide whether you want to have medical male circumcision. However, in some cases, the risks of not being circumcised can be greater than the risks of the operation itself. Examples of such cases include adults who have a condition that requires a circumcision and those at a higher risk of developing certain conditions that medically male circumcision can prevent. The decision of having the procedure done should be made with the help of a trusted healthcare professional. Always seek medical advice if you have any doubts regarding whether you or your child should proceed with this elective surgical procedure.
Will a medical male circumcision improve my sex life?
Although many men report an improvement in sexual satisfaction after being circumcised, the relationship between circumcision and sexual function has not been fully established. As noted in a report produced by the World Health Organization, male circumcision has been shown to lead to safer, more satisfying sex for both men and their partners. This is because male circumcision has been shown to lead to a marked decrease in the risk of developing sexually transmitted infections, including HIV. Also, some studies have shown that male circumcision is associated with a decreased risk of developing penile cancer and a reduced risk of cervical cancer in female sex partners. However, as with any operation, there are risks that need to be taken into consideration and it may be some weeks before the full benefits of male circumcision are noted. For example, immediately after the surgery the glans (or head) of the penis may appear sensitive. However, this should subside as the area becomes less exposed and the glans becomes less sensitive. Also, during the healing process there may be some temporary side effects, but these are typically mild and easily treatable. For example, from time to time men may experience minor discharge of urine onto the wound and there is a possibility of a minor wound infection occurring. However, this can normally be treated using an antibiotic spray or ointment. Although infections can occur, more serious complications such as excessive bleeding or damage to the tube that carries urine from the body have been noted as being extremely rare. Patients need to be made fully aware of any risks that are involved with male circumcision and they need to know how to find help if anything goes wrong. Also, some patients may experience post-operative bleeding which may occur a few hours after surgery. If the bleeding is only slight, changing the dressing and applying pressure may help. However, removal of the stitches and surgical exploration of the wound may be necessary if the bleeding is more severe.
Will a medical male circumcision increase the size of my penis?
It is a common misconception that removal of foreskin might result in the penis looking longer. Technically speaking, we can see the entire length of the penis after circumcision, but this does not mean that the penis looks longer. The fact of the matter is that the medical male circumcision technique prefers removing the inner layer of the foreskin and leaving the outer layer. The « circumcision swelling » and the tight wound post-circumcision would suggest that the penis appears longer when it is in fact swollen. In other words, any change in size is not permanent. When the body recovers and the wound is healed, the penis will return to its original size. Short-term changes are probably attributed to the surgical techniques used in circumcision. Dr. Banghao Chen has provided 2D and 3D computer modelling studies in 2001 to 2002 that penile length remained unchanged after undertaking medical male circumcision surgery. His work has been published in Journal of Urology, which concludes that « adult penile length remains unchanged post-circumcision ». Ergo, Dr. Chen suggested that circumcision has no effect on penile size. Professor Van Howe has outlined this evidence in his booklet/board, which is probably why the NHS, the BMA and many official health organisations in the world do not advocate the idea of circumcision to enhance penile size. On the other hand, circumcision may improve the sexual health. Studies published by the World Health Organisation show that male circumcision can reduce the risk of certain sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV. However, more studies are required to establish the long term safety issue and health benefits of circumcision if there is any. Ergo, it is recommended to maintain a good genital hygiene and a present monogamous sexual lifestyle. Sexual health should come first instead of other commercial and non-medically justified operations. Ergo, it is recommended to maintain a good genital hygiene and a present monogamous sexual lifestyle. Sexual health should come first instead of other commercial and non-medically justified operations.
Will a medical male circumcision increase the size of my penis?
There is contradictory, non-evidence-based information on the internet about the potential sexual and psychological benefits of the surgery, including suggestions that having a circumcision can increase the size of a man’s penis. However, it is important to note that there is no scientific evidence to support such claims. An adult circumcision will not make your penis larger if it is done in later life. Penis size is not a valid medical indication for medically necessary circumcision for a man of any age. As with any surgical procedure, general anesthesia carries small but significant risks. As in any tissue injury resulting from surgery or trauma, scar tissue can form and this may lead to a general tightening of the skin in the pubic area. This might affect the comfortable flaccid length of the penis. However, there are many men who are uncircumcised and have significant amounts of tight foreskin during erection, and they, and their partners, are perfectly happy with their sex life. There are no proper studies demonstrating that penile sensation is affected after medical male circumcision. In some African randomized controlled trials, researchers have found that circumcised men have a small decreased risk of getting sexually transmitted infections including HIV. This might be due to the fact that the inner skin of the foreskin is more prone to infection and micro trauma. However, it is unknown whether the pattern of tissue injury through micro trauma in the inner skin of the foreskin is the same as traumatic injury leading to hypertrophy of scar tissue in the penile shaft skin (the skin that is removed during a circumcision). We have no idea whether the skin removed during a medically necessary circumcision is involved in sexual response or function at all. Mainly, medical male circumcision is offered for those who have certain medical conditions of the foreskin or the private parts. The commonest reasons could be recurrent attacks of infection of the foreskin and the penis, or a difficulty retracting the foreskin to pass urine or to wash. Some people might need surgical correction of the curve of the penis as well. The surgery can be carried out under local anesthetic, which is commonly available in an outpatient clinic.
When do they take out the stitches after my medical male circumcision?
Circumcision stitching is typically performed using absorbable stitches, which means that they do not need to be removed. Your doctor will cover the stitches with an ointment and a gauze dressing, which is usually taken out after 24 hours. After this, it is important to keep the wound clean and dry, so avoid picking at or touching the stitching. It is also advisable to wear loose underwear and trousers to reduce irritation of the wound area. This will help to minimize the possibility of infections and other complications. Although circumcision stitching can cause slight pain or discomfort, it usually heals within one to two weeks after the procedure. If you notice any persistent bleeding, worsening pain, or a discharge from the wound, you should see a doctor for advice. Care should be taken to avoid situations where the wound may become submerged in water, as this can also lead to infection. For example, you should avoid activities such as swimming until the wound is fully healed. If non-absorbable stitches have been used, these are removed in the clinical setting after seven to ten days. All the skin which covers the penis is removed during circumcision, including the foreskin. The entire procedure takes around 30-60 minutes. Although absorbable stitches do not need to be removed, the healing process for someone who has stitches after circumcision will be broadly the same. Absorbable stitches can increase the chances of excessive scar tissue formation, such as a keloid or hypertrophic scar, after the wound has healed. This may result in the necessity for further treatment down the line, so always report any unusual changes in the appearance of the wound to your doctor. Excessive scar tissue may also be more likely to cause irritation in the years after the circumcision has taken place. If there is excessive or uncomfortable scarring, a treatment called a preputioplasty may be available. This is a minor surgical procedure which effectively re-opens the foreskin, allowing natural cleaning of the penis to take place.
How long before I can have sex again after a medical male circumcision?
Sex should be avoided for about four weeks after a medical male circumcision. This is to allow full healing and to reduce the risk of complications. Even though you may start to feel more comfortable after the first week, it is essential to keep dust and contamination out of the wound. Your circumcision wound will usually take between 7 to 10 days to heal, although everyone is different and it may take longer. After this, it should be fairly safe to do light activities and return to work or school. However, using a condom and a lubricant before having sex is recommended for the first few times. A circumcision is a surgical procedure that removes the foreskin (the loose tissue) covering the glans of the penis. Nowadays, medical male circumcision is also carried out for the following reasons: to reduce the risk of getting some infections, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as HIV; to reduce the risk of conditions that can develop in later life, such as balanoposthitis and phimosis. These are rare and occur when the foreskin can’t be pulled back over the head of the penis.
Who can have medical male circumcision?
In several African countries, defined age ranges have been set for medical male circumcision. It is largely recommended to be done for children within 10-14 years of age for its maximum rational health benefit. In Kenya, for example, medical male circumcision is done as a routine national health policy for all male neonates and children at public hospitals. Even though the national policy on voluntary medical male circumcision doesn’t talk about age limit, it’s quite evident that it’s way much safer to perform circumcision on children of two years and below who wouldn’t remember the pain and could have better wound healing than performing it on adults. In most cases, men may seek circumcision for various personal reasons such as religion, culture, beliefs and practices, maintaining better genital hygiene, and promoting sexual health. However, parents are the key decision-makers on matters of circumcising baby boys, and their consent is required prior to the procedure. Every potential male circumcision candidate must undergo a thorough medical assessment to ascertain his eligibility for the operation. For example, the healthcare provider shall take a detailed medical history of the client and provide accurate counseling in line with the country’s medical male circumcision guidelines. As such, the person must be willing to undergo the procedure and appreciate the possible risks and complications that may be associated with medical male circumcision. These interventions give room for significant accidental findings and diagnoses that may need attention and management or exclusion of the candidate for the operation. With informed consent having been granted, the candidate will be taken through a well-described and clearly documented medical male circumcision procedure by a qualified medical doctor licensed by the national medical practitioners and dentist board in Kenya. Adolescents are able to consent for themselves provided they understand the nature and purpose of the operation and have been well informed about the procedural risks and benefits. Reproductive healthcare service providers should seek to acquire detailed knowledge, develop skill, and change clinical practices in order to give quality and wholesome care to patients, especially on the discipline of male circumcisions. Every practitioner should regularly review research evidence on medical male circumcision and apply the findings in their day-to-day work to ensure complete patient satisfaction and achievement of the populous health policy goals. That is conclusive evidence that points out to the continuous character of what we may call an organized professional training for improvement and upholding of people’s wellness through male medical circumcision interventions. Every professional should aim at systematically collecting, appraising, and applying research findings in patient care, teaching of the juniors, and putting off lectures and professional development as enshrined in the medical practitioners and dentist board code of conduct under the clinical practices. Respective individuals of the board are expected to guide serious professional practice by keeping up to the healthcare system’s knowledge and continuous training so as to ensure that better treatments, healthcare services, and outcomes are realized. The authentic objective of medical male circumcision as a procedure for preventing papilloma virus and human immunodeficiency virus transmission in the procreative life has been raised on many scientific grounds and objective commentaries. These include systematic low bias studies and reviews with a big sampling frame such as the World Man Health Organization’s trial results on the higher preventive effect to females through male circumcision in the reduction of cervical cancer, among others.

