What Is Dental Bone Grafting and Why Do We Use It?
What Is Dental Bone Grafting and Why Do We Use It?
Dental bone grafting is a crucial procedure in modern dentistry, addressing the problem of bone loss in the jaw, which can occur due to tooth loss, periodontal disease, or other factors. This procedure involves using a bone graft to replace or augment missing bone in the jaw, providing a stable foundation for future dental implants or other restorative procedures. Understanding what is a dental bone graft and its purpose helps us appreciate its importance in oral health care.
Why Does Tooth Loss Cause Bone Loss?
Tooth loss leads to bone loss because the jawbone relies on the stimulation from teeth to maintain its density and strength. When a tooth is lost, the lack of stimulation causes the bone to deteriorate, a process known as resorption. Over time, this can lead to significant bone loss, affecting the structure of the jaw and the stability of remaining teeth. Is a tooth a bone? No, a tooth is not a bone, but it is connected to the bone in the jaw, and their health is interdependent. Therefore, replacing missing teeth with implants often requires a dental bone graft to ensure there is enough bone to support the new implant.
How Do Bone Grafts Work?
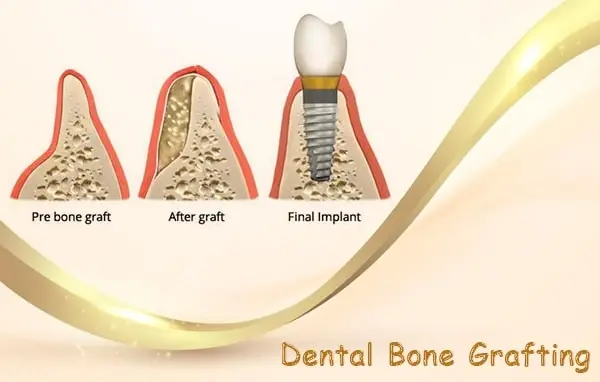
A bone graft works by providing a scaffold onto which new bone cells can grow. This process, known as osseointegration, is essential for the success of dental implants. There are different types of bone grafts, including autografts (using bone from the patient’s own body), allografts (using bone from a donor), xenografts (using bone from an animal, typically a cow), and alloplasts (using synthetic materials). Each type has its own advantages and is chosen based on the specific needs of the patient. The bone grafting dental procedure involves placing the graft material at the site of bone loss, where it encourages new bone growth and integrates with the existing bone.
The specific steps involved in a dental bone grafting procedure can vary, but they generally include the following: First, the dentist or oral surgeon will make an incision in the gum to expose the bone. The bone graft material is then placed at the site, and a membrane may be used to cover the graft and promote healing. The incision is closed with stitches, and the area is allowed to heal over several months. During this healing period, the bone graft dental material serves as a framework, allowing new bone cells to grow and fill in the defect.
What Happens After a Bone Grafting Procedure?
After a bone grafting for dental implants procedure, the healing process begins. Initially, there may be some discomfort, swelling, and minor bleeding, but these symptoms usually subside within a few days. Pain management typically involves over-the-counter pain relievers, although stronger medications may be prescribed if necessary. It’s crucial to follow the dentist’s post-operative care instructions, which may include avoiding certain foods, maintaining good oral hygiene, and possibly taking antibiotics to prevent infection.
The bone graft before and after comparison shows significant improvement in bone volume and density. It can take several months for the graft to fully integrate with the existing bone. During this time, the new bone cells gradually replace the graft material, creating a strong and stable bone structure. This process is vital for the stability of future dental implants.
Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor the progress of the oral bone graft and ensure that the healing is proceeding as expected. The dentist will take X-rays or other imaging studies to evaluate the integration of the graft and the development of new bone. In some cases, additional procedures may be necessary if the initial bone graft does not fully integrate or if more bone is needed.
Who Needs Bone Grafts?
Bone grafts are necessary for patients who have experienced bone loss in the jaw. This can result from tooth loss, periodontal disease, trauma, or congenital defects. Individuals who plan to receive dental implants but lack sufficient bone density or volume are prime candidates for a bone graft for implant. Additionally, patients who have suffered from severe gum disease might require a bone graft dental to restore the lost bone around their teeth. Essentially, anyone with compromised jawbone health may benefit from dental bone grafting to rebuild and strengthen their jawbone.
Another group that may need bone grafts includes those undergoing certain orthodontic treatments. In cases where teeth need to be moved significantly, bone grafts can provide the necessary support for proper alignment. Furthermore, patients with facial injuries or congenital deformities may require bone grafting to restore normal function and appearance.
In some cases, even people without immediate plans for dental implants might benefit from a bone graft. For instance, if a tooth has been extracted and the surrounding bone is thin or weak, a graft can help preserve the bone for potential future restorative options. Overall, bone grafts play a vital role in maintaining oral health and ensuring the success of various dental treatments.
Bone Grafting is Normal
Bone grafting is a common and routine procedure in dentistry. Many people undergo this procedure to improve their oral health and ensure the success of dental implants. Advances in dental technology and techniques have made bone grafts highly effective and predictable. Understanding that bone grafting dental is a standard part of restorative dentistry can help alleviate any anxiety or concerns patients may have. The use of bone grafts helps restore not only the function but also the aesthetics of the jaw and teeth, leading to improved overall oral health.
The materials used for bone grafts are biocompatible and safe, with a long history of successful use in dental and medical procedures. Modern techniques ensure that the risk of complications is minimal, and the benefits far outweigh the potential risks. Patients can be confident that dental bone grafting is a well-established procedure that can significantly enhance the outcome of their dental treatments.
Do You Need a Bone Graft Before Getting Dental Implants?
The need for a bone graft before getting dental implants depends on the individual’s jawbone condition. If there is sufficient bone density and volume, a bone graft may not be necessary. However, if the jawbone has deteriorated or lacks the necessary support for an implant, a bone graft in mouth is required. The dentist will assess the patient’s bone structure using imaging techniques to determine if a bone graft dental implant is needed. The goal is to create a stable and robust foundation for the implant, ensuring its long-term success and functionality.
Understanding what is a bone graft and its role in dental health is vital for those considering dental implants or dealing with bone loss in the jaw. Dental bone grafting is a highly effective procedure that can restore bone density, support dental implants, and improve overall oral health. By addressing bone loss through bone grafts, patients can achieve better dental outcomes and enjoy the benefits of a strong, healthy jawbone. Whether it’s a bone transplant for dental implants, jaw bone graft, or tooth bone graft, the advancements in bone augmentation have made these procedures an integral part of modern dentistry.

